THERMODYNAMIQUE (F)
Section outline
-
-
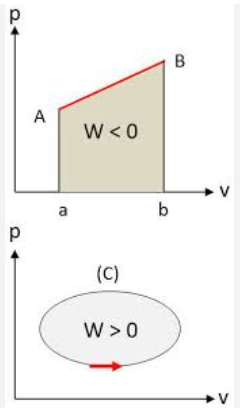
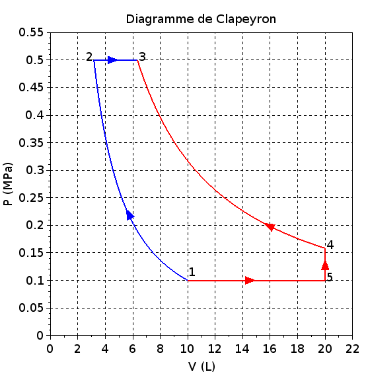
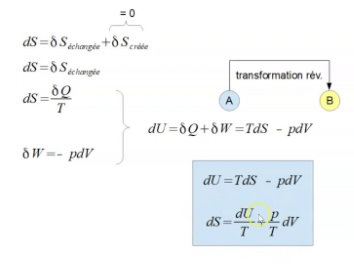
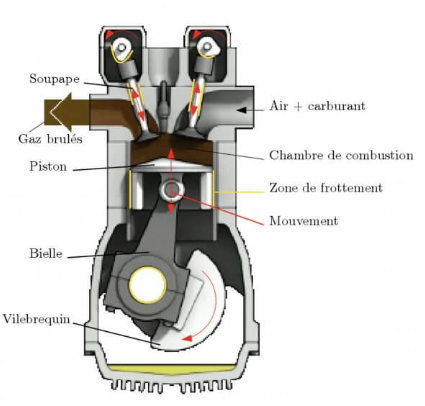
Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with the relationships between heat, work, and energy. It explores how energy is transferred between different forms and how it affects the physical properties of matter. At its core, thermodynamics seeks to understand and quantify the behavior of systems undergoing changes in temperature, pressure, and volume. It encompasses fundamental concepts such as energy conservation, entropy, and the laws of thermodynamics, which govern the direction and efficiency of energy conversion processes. Thermodynamics has applications across various fields, including engineering, chemistry, biology, and environmental science, playing a crucial role in understanding and designing systems ranging from engines and refrigerators to living organisms and the universe itself.

-
[1] Elie Tawil, M.S., Leed AP, DOE Fundamentals Handbook, Thermodynamics, Heat Transfer, and Fluid Flow, Volume 1 of 3.U.S. Department of Energy Washington, D.C.20585
[2] Olivier Perrot, Cours de Thermodynamique, I.U.T.de Saint-Omer Dunkerque Département Génie Thermique et énergie, 2011.
3] Cengel Yunus, Thermodynamics an engineering approach, John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 1st edition, 2010.
[4] MichaelJ.Moran, Howard N. Shapiro, Fundamentals of engineering thermodynamics, John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 5thedition, 2006.