Physics 1: Mechanics of a Material Point
Résumé de section
-
University: Djilali Bounaama Khemis Miliana
Faculty: Science and Technology
Department: Material Sciences
Domain: Sciences and technology
Level: L1
Module: Physics I : Dynamics.
Semester: 01 (15 weeks).
Coefficient: 03
Credit : 06
Semester hourly volume: 67h30 min
Weekly hourly volume: 4h30 min (3h00 min lessons and 1h30 min tutorial)
Lecturer: Dr. ELBAA Mohamed.
specialty: Materials Physics
Diploma: Doctor in pharmaceutical analysis
Grade: MCB
Contact: m.elbaa@univ-dbkm.dz.
Assessment method: The evaluation is carried out through an interrogations and a Final Exam.
To pass the module, the general average must be greater than or equal to 10 out of 20
-

Studying kinematics and dynamics enables us to comprehend how objects move and the forces influencing their motion. Through this study, students develop problem-solving skills applicable across various fields, including engineering and physics. Engineers utilize these principles to design efficient and safe systems, while scientists employ them to understand natural phenomena and formulate theories.
-
Notion of vector analysis (scalar and vector field, integrals: one-dimensional, two-dimensional and three-dimensional, gradient, divergence, rotational).
-
I. Chapter 0 : Mathematical reminders:
1- Equation for dimensions.
2- Reminder on vectors
II. Chapter I : Kinematics :
1‐ Position vector in coordinate systems (Cartesian, cylindrical, etc.) - law of motion - Trajectory.
2‐ Velocity and acceleration in coordinate systems.
3‐ Applications: Movement of a material point in different coordinate systems.
4‐ Relative motion.
III. Chapter II. Dynamics :
1‐ Generalities : Mass ‐ Force ‐ Moment of force – Absolute and Gallilien reference frame
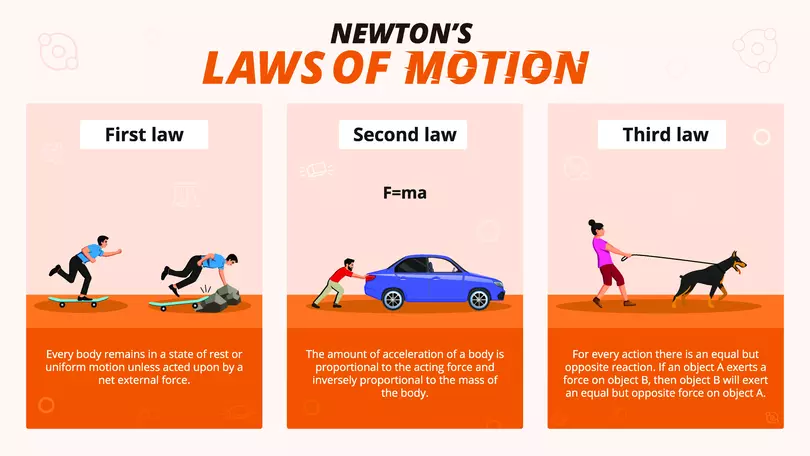
2‐ Newton's laws
3‐ Principle of conservation of momentum.
4‐ Differential equation of motion
5‐ Kinetic momentum
6‐ Applications of the fundamental law for forces (constant, time-dependent, velocity-dependent, central force, etc.).
IV. Chapter III. Work and energy :
1‐ Work of a force
2‐ Kinetic energy
3‐ Potential energy – Examples of potential energy (gravity, gravitational, elastic)
4‐ Conservative and non-conservative forces – Total energy theorem
V. Bibliography
-
1. Gibaud, M. Henry ; Cours de physique – Mécanique du point – Cours et exercices corrigés ; Dunod, 2007.
2. Marcelo Alonso, Edward J. Finn; Fundamental university physics, Volume 1: Mechanics (Addison-Wesley series in physics) Hardcover – January 1, 1967
3. P. Fishbane et al.; Physics For Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, 3rd Ed. ; 2005.
4. P. A. Tipler, G. Mosca ; Physics For Scientists and Engineers, 6th Ed., W. H. Freeman Company, 2008.