Chimie Organique 2
Section outline
-
University: Djilali Bounaama Khemis Miliana
Faculty: SMI
Specialty: Chemistry
Level: L2 Licence
Module: Organic chemistry 2
Semester: 2
Coefficient: 3
Lecturer: Dr. CHERIFI Souad.
specialty: Water and Environment
Diploma: Doctor in Process Engineering
Grade: MCB
Contact: You can contact me on s.cherifi@univ-dbkm.dz
Assessment method: Continuous Assessment: 33%, Final Examination: 67%
-
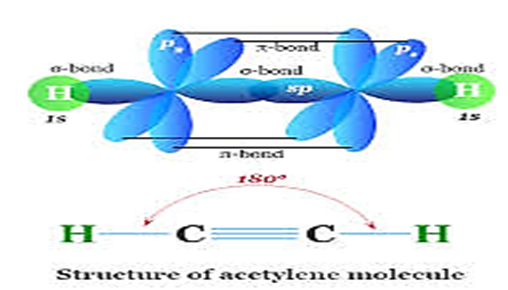
This course explores the fundamental principles of chemical bonding in organic molecules, focusing on the types of bonds, their formation, and their influence on molecular structure, stability, and reactivity. Students will learn about covalent bonding, hybridization, resonance, and intermolecular forces, applying these concepts to predict and explain the behavior of organic compounds.
-
This course provides a comprehensive study of electronic effects in organic molecules, focusing on how electron distribution influences molecular structure, reactivity, and spectroscopic properties. Students will explore inductive, resonance, hyperconjugation, and steric effects, along with their applications in predicting reaction mechanisms, stability, and regioselectivity.
-
This advanced course provides a systematic framework for classifying, analyzing, and predicting organic reactions. Students will develop expertise in:
Recognizing fundamental reaction patterns
Applying mechanistic principles to complex transformations
Utilizing modern tools for reaction analysis
-
This advanced course provides a deep dive into the fundamental processes that govern organic transformations. Students will:
Master arrow-pushing formalism and electron-flow analysis
Develop skills to propose, analyze, and validate reaction mechanisms
Learn to connect molecular structure with reactivity patterns
Apply kinetic and spectroscopic tools for mechanistic studies
-
This course provides a comprehensive study of hydrocarbons, the fundamental building blocks of organic chemistry. Students will explore the structure, nomenclature, physical properties, stereochemistry, and reactivity of:
Alkanes & Cycloalkanes (saturated hydrocarbons)
Alkenes (unsaturated hydrocarbons with C=C bonds)
Alkynes (unsaturated hydrocarbons with C≡C bonds)
The course emphasizes molecular structure, conformational analysis, and reaction mechanisms, preparing students for advanced organic chemistry and practical applications in petrochemicals, polymers, and pharmaceuticals
-
This advanced course explores the unique world of aromatic compounds, focusing on their structure, bonding, and distinctive reactivity. Students will:
Master Hückel’s rule and aromaticity criteria
Analyze electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) mechanisms
-
Unique reactivity patterns (C-X bond transformations, metal-carbon bonds)
Applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and catalysis
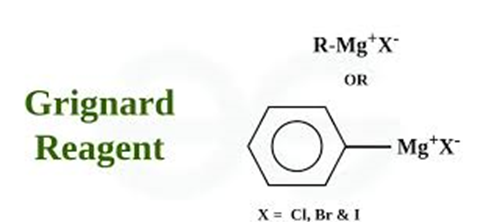
This course explores the structure, properties, and synthetic utility of halogenated hydrocarbons and organometallic compounds, emphasizing their:
-
This chapter covers the structure, nomenclature, properties, and reactions of alcohols, phenols, and ethers, which are important classes of organic compounds containing oxygen.

