CHAPTER III: PARTICULARITIES OF PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS AND THE ESSENTIAL CRITERIA
Résumé de section
-
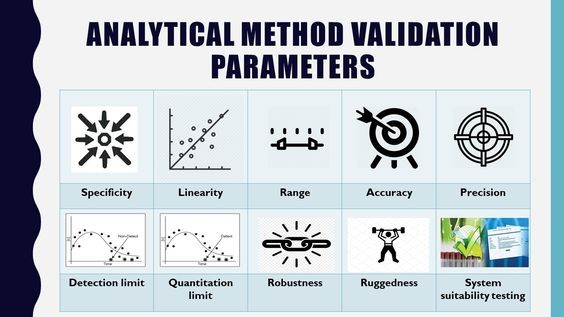
Pharmaceutical analysis involves the analytical signals treatment and transformation into data concerning the nature and amount of a substance, its chemical structure or spatial location of the sample - important components that require statistical treatment to have any real value. According to pharmacopoeial and GMP requirements, the analytical procedures used for drug quality control must be validated to confirm experimentally that they provide relevant and reliable information about the object of analysis and are suitable for their intended purpose. All quantitative tests, including impurities limit tests, should be validated, as should identification tests if it is necessary to confirm their specificity. The validation of analytical procedures is regulated by various national and international standards (ICH), which evaluate characteristics such as accuracy, precision, specificity, detection limit, quantitation limit, linearity, range, and robustness. Strict adherence to these validation parameters is essential to ensure the reliability and integrity of pharmaceutical analysis, which is critical for product quality, safety, and efficacy.


